WEEK 8 LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Day 1
- State the two causes of control hazards.
- Describe the effect of unconditional and conditional
branches on pipeline performance.
- List the two principal techniques used to handle
control hazards.
- Justify advancing jump circuitry into earlier pipeline
stages such as IF or ID.
- Draw pipeline flight plans showing instructions
stalling through branch decision and then flushing after a taken branch.
- Compare and contrast the simple
(predict branch not taken) and complex (statistical prediction) branch
prediction techniques.
- Comment on the success of state-of-the-art branch
Day 2
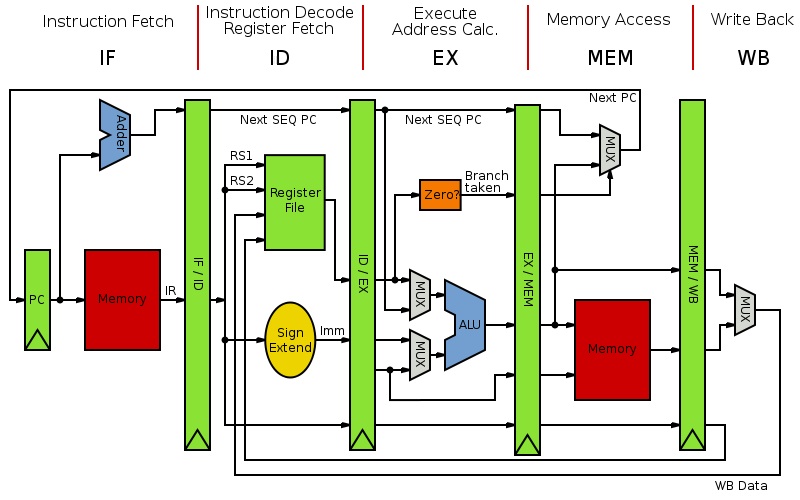
- State the names of the pipeline registers in a
basic ARM pipeline without interlocked stages.
- State the signal groups that are held in each
pipeline register in a basic ARM pipeline without interlocked stages.
- Identify ALU sources for ARM pipeline
microarchitectures that include forwarding circuitry for data hazard
elimination.
- Draw the ARM pipelined microarchitecture.
Day 3
- Draw the ARM pipelined microarchitecture.
Do it again!
- State what ARM means as an acronym.
Explain the ARM acronym.
- Describe the design requirements of the ARM pipeline
data hazard forwarding controller.
- Describe the design requirements of the ARM control
hazard stall and flush controller.